The bed file looks like this:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
SM_V7_1 323629 324345 SM_V7_1#2 40 +
SM_V7_1 1215610 1253189 SM_V7_1#3 40 +
SM_V7_1 1215631 1253205 SM_V7_1#4 40 +
SM_V7_1 1220420 1253192 SM_V7_1#5 40 +
SM_V7_1 1220506 1253206 SM_V7_1#6 40 +
SM_V7_1 1220507 1245199 SM_V7_1#7 40 +
SM_V7_1 1220507 1253205 SM_V7_1#8 40 +
SM_V7_1 1220507 1253205 SM_V7_1#9 40 +
SM_V7_1 1220507 1253205 SM_V7_1#10 40 +
...
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1107 40 -
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1152 40 -
SM_V7_1 3867143 4060784 SM_V7_1#1309 40 -
SM_V7_1 3867151 4060784 SM_V7_1#1398 40 -
SM_V7_1 3867245 4060765 SM_V7_1#1454 40 -
...
|
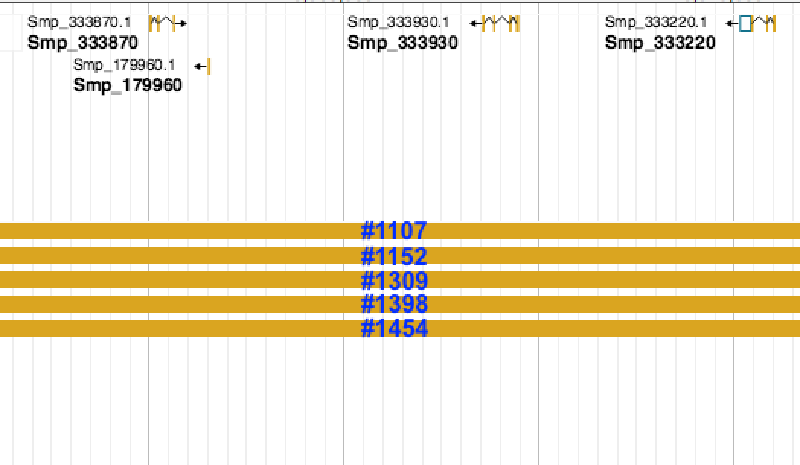
Note that there are quite many duplicate features from different reads. I don’t want to remove the duplicate features at this step because I need the information about counts in the late merge step. For now I would like to remove those extra long reads, which normally mapped to several genes in the annotation, eg. #1107 to #1454. I have tried several tools:
gffcompare
It’s one of my favourite tools to find overlaps between two annotation files. So I did:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
awk '{print $1, "isoseq", "gene", $2, $3, $5, $6, ".", "ID=" $4}' prefiltered_mergedIsoseq.bed| tr ' ' '\t' > Filter_isoseq.gff
~/Tools/gffcompare/gffcompare -r Filter_isoseq.gff -T -o Filter_v7.3 ../../Smv7.3/Sm_v7.3_Basic-noGaps.gff
grep '#' Filter_v7.3.annotated.gtf | awk '{print $14 "\t" $12}'| tr -d \" | tr -d \; | sort -u | awk '$1!=p{if(p)print s; p=$1; s=$0; next}{sub(p,x); s=s $0} END{print s}' | awk '$3>0'|tr '\t' ','| sed 's/,/ /' | head
Which shows me the isoseq reads that overlapped with multiple genes:
~~~~~~
SM_V7_1#10831 Smp_167310,Smp_325900
SM_V7_1#11383 Smp_173250,Smp_173280
SM_V7_1#1152 Smp_067060,Smp_103610,Smp_179960,Smp_326440,Smp_333220,Smp_333870,Smp_333930,Smp_334070,Smp_334170,Smp_334240
SM_V7_1#11806 Smp_141290,Smp_141390
~~~~~~
We can see that #1152 was spotted but the others were not. Even with *-A* option I couldn't find any information about eg. #1107
### bedtools
There are two functions in bedtools: intersect and overlap
#### intersect
```bash
bedtools intersect -wo -a prefiltered_mergedIsoseq.bed -b Sm_v7.3.bed
|
Which nicely gave all reads mentioned above. Note that the last column is the number of base pairs of overlap between the two features.
1
2
3
4
5
|
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1107 40 - SM_V7_1 3867138 3869857 Smp_103610 . - 2716
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1107 40 - SM_V7_1 3887599 3889162 Smp_333870 . + 1563
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1107 40 - SM_V7_1 3891316 3891601 Smp_179960 . - 285
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1107 40 - SM_V7_1 3908953 3911250 Smp_333930 . - 2297
SM_V7_1 3867141 4060784 SM_V7_1#1107 40 - SM_V7_1 3925420 3927716 Smp_333220 . - 2296
|
overlap
1
|
windowBed -a prefiltered_mergedIsoseq.bed -b Sm_v7.3.bed | bedtools overlap -i stdin -cols 2,3,8,9
|
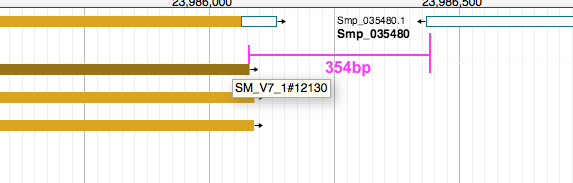
gave nearly the same results as above, except that it also showed the distance between nearby features on the opposite strands. For instance:
SM_V7_1 23952758 23986080 SM_V7_1#12130 40 + SM_V7_1 23986434 23992052 Smp_035480 . - -354